Remote Services in After Sales - Advantages and Use Cases
From installation and maintenance to troubleshooting: The year 2020 in particular has shown that these services are also possible remotely - i.e. without on-site presence. Even complex problems can be solved by remote support.
#1 Installation and updates
When new machines or systems are taken into operation, modern technology means that it is no longer absolutely necessary for a service technician from the manufacturing company to be present on site. Depending on the complexity, the operator of the machine can perform the necessary steps for commissioning himself via easy-to-understand (video) instructions or supported by virtual live support. Certain maintenance processes, such as software updates, can be carried out entirely remotely. What is already common practice in IT administration is increasingly finding its way into mechanical and plant engineering. For this purpose, the service technician must connect securely to the relevant machine and trigger the update processes.
#2 Monitoring
The permanent monitoring of a machine or plant with the help of sensors and Smart Connected Services is an essential use case for Remote Services. Errors or anomalies are automatically transmitted to the manufacturer and the necessary troubleshooting processes are triggered. For example, it may be necessary to replace a specific spare part or perform maintenance. Monitoring is also an essential foundation for implementing tactical maintenance strategies, such as condition-based maintenance or predictive maintenance. Compared to predictive maintenance, condition-based maintenance only takes action when a certain threshold is exceeded. With predictive maintenance, this already happens when the measured values move in the direction of the threshold value.
#3 Troubleshooting
Under certain conditions, remote services are also worthwhile in the area of eliminating malfunctions. For example, the service technician can support the employee on the customer side by video call via smartphone, tablet or with the help of smart glasses during troubleshooting and error correction and instruct him precisely.
Through the screen transmission, the service technician takes the same point of view as the customer, which facilitates this process. At the same time, depending on the technology used, the service technician has the option of using a digital laser pointer or making notes to highlight certain areas in the image. The advantage of data glasses compared to smartphones and tablets is that the employee on the customer side has both hands free to carry out the guided actions.
This leads to time and cost savings as traveling is eliminated and problems are quickly resolved. This reduces downtime to a minimum. The use of augmented reality (AR) technology additionally makes it possible, for example, to display machine-relevant data or step-by-step instructions as well as to look digitally inside the machine. This requires an integrated system in which the machine's service data is stored and from which it can be retrieved.
#4 Onboarding of new customers and trainings
On-the-job trainings and onboarding of new customers are increasingly done via remote services using smart devices (tablet, smartphone or smart glasses) or via tutorials. Traveling to the customer is not always possible or practical. Even for employee training, not all people are at the same location. In addition to increasing efficiency, this aspect has a positive impact on the carbon footprint of the manufacturing company. In this way, you not only help your after-sales-service to develop an innovative image, but also a sustainable one.
Advantages of Remote Services in After-Sales and Service at a glance:
- Elimination of travel time
- Fast problem solving and support
- Shorter downtimes
- Higher customer satisfaction
- Increased efficiency in service
- New business models in customer service
- Reduction of CO2 emissions by eliminating the need to travel
Which tools and systems are necessary and useful for remote services?
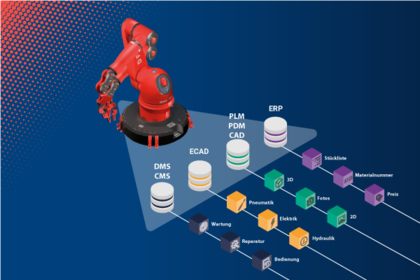
In addition to digital devices such as tablets, smartphones, smart glasses or similar, service technicians and customers need access to a system in which the service-relevant information of the machine or plant is stored: In a service information system, they receive a 360° service view of the information they need to identify the malfunction or rectify the problem - precisely from this machine, which is in use by this customer. Directly at the Point of Service Need. This gives service technicians and customers 3D and 2D views of the assemblies, information on spare and wear parts, access to the relevant part of the technical documentation, schematics, video instructions, hydraulic or pneumatic diagrams, and much more. All bi-directionally networked and easy to find.
Furthermore, the customer needs a solution to contact the service technician at the manufacturer, to chat with him, to make a live video call or to request remote maintenance.
Conclusion: Remote services support after-sales and service
Depending on the complexity of the machines and equipment, offering remote services can be useful and purposeful for manufacturers. Particularly if it is easily possible to support technicians on the customer side through virtual technologies and live instructions. If specialized knowledge or special tools are required, remote services may not be sufficient to perform maintenance or resolve malfunctions. The longer and more expensive the travel time to the customer, the more worthwhile remote services can be.