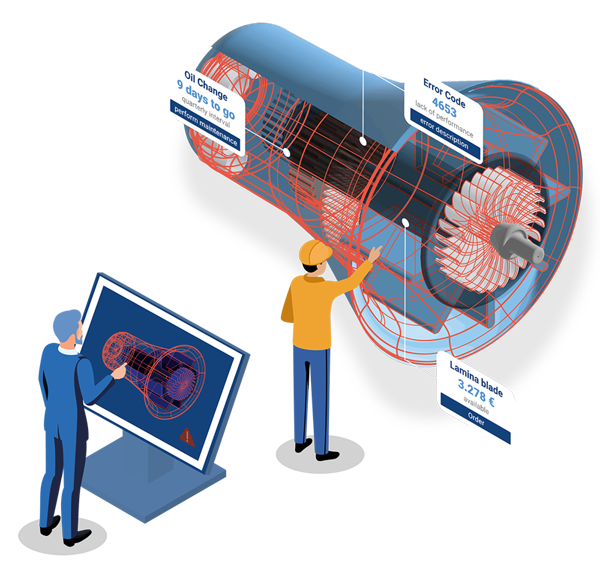
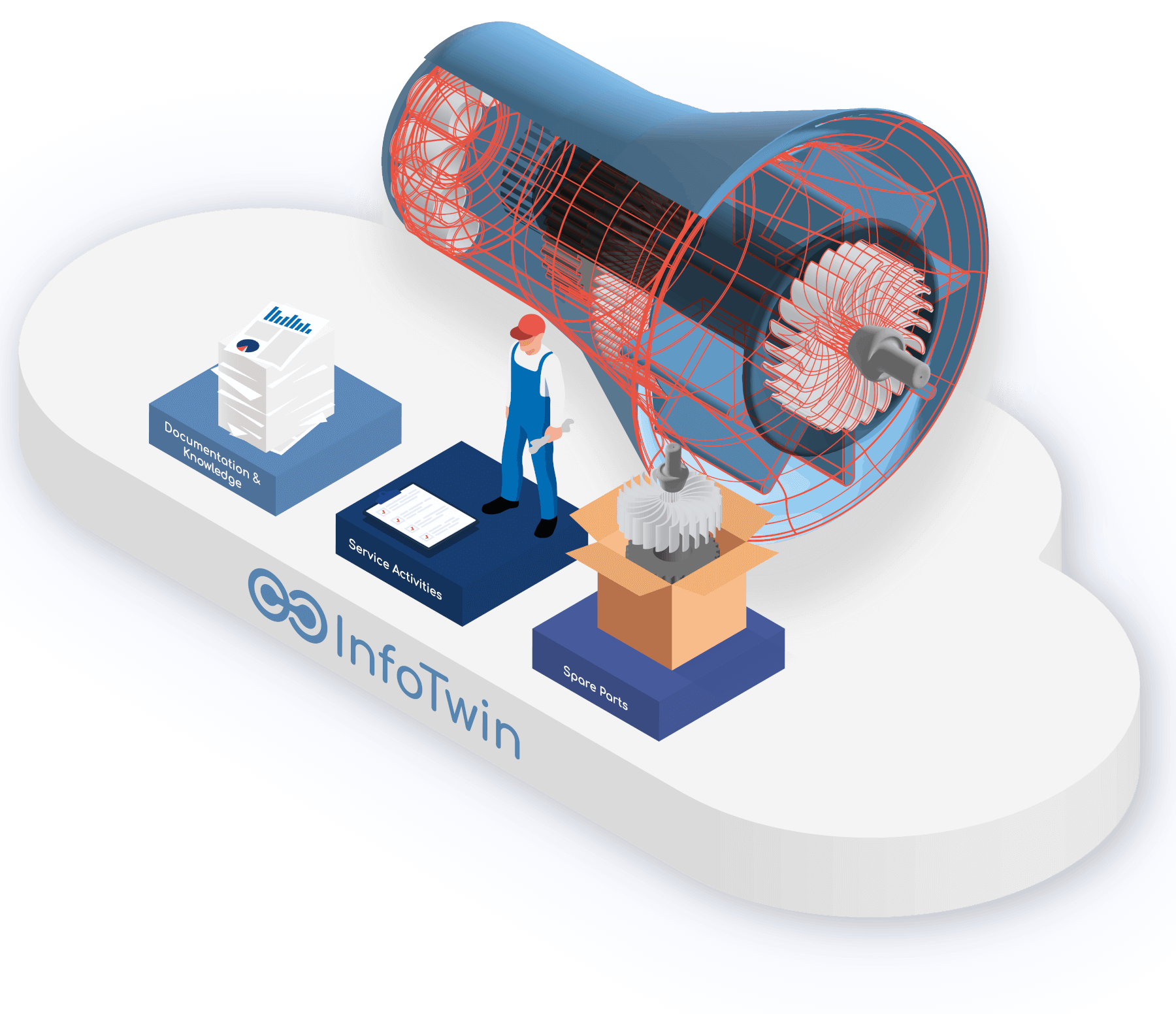
The modular cloud solution ensures the intelligent networking and provision of product documentation, spare parts and service information – and in so doing helps you find what you've been looking for: the right spare part, the right service instructions, or information on consumables that will soon be required. Quanos InfoTwin provides the content you need for efficient aftersales & service processes.
As a manufacturer and operator of machines and plants, you gain valuable insights regarding the status of your assets, as well as a central database for aftersales & service. As a standardized out-of-the-box solution, Quanos InfoTwin is ready to use immediately, with the possibility of modular expansion. Easy to operate, the cloud solution links all relevant information for the aftersales & service process to a digital information twin. It thus effortlessly creates the basis for new business models and smart services.
- Based on experience from over 1,100 customer projects
- No need for your own IT resources
- Cloud-native: no installation required, software can be used straight from your browser
- Always the latest features and updates at regular intervals
- Highly scalable and future-proof thanks to modularity
- Standard software for a quick start and easy operation
- Easy access to quickly tap into initial efficiency potentials
- Easy (automatic) connection of data from various sources systems with no IT costs
- Low risk and no commitment, thanks to SaaS functionality
- Modular yet easy to expand at any time
- Access to tried-and-tested & packaged modules based on years of experience
- Benefit from reliable data structures, processes, and functionalities for information management
- Based on experience from over 1,100 customer projects
- No need for your own IT resources
- Cloud-native: no installation required, software can be used straight from your browser
- Always the latest features and updates at regular intervals
- Highly scalable and future-proof thanks to modularity
- Provision of all the necessary aftersales and service information - worldwide availability 24/7 for all users via a browser
- Additional income through digital value-added services, e.g., through data provision via the TwinAPI
- New business and accounting models (SaaS, subscription, etc.) based on analytical information on assets

„The plan to set up a single source of documentation was a complete success and we were able to move past the data silos and the inefficiencies that came with them. The QR code on their Güdel product provides our customers with a direct, digital means of accessing the technical documentation.“
Güdel Group AG Jürgen Stitz, Documentation Manager, Güdel AG

„With InfoTwin, an information source has been created that can simplify the work not only of the customer, but also of the fitter or service technician, for example. Whether it's spare parts or maintenance work for the customer and service technician, or assembly or transport of the machine for the fitter, the bundled and filterable information means that many can benefit from the information provided by the InfoTwin at the same time.“
MINDA Industrieanlagen GmbH Lena Bredemeier | Technical Editor

„It was a great feeling when the system displayed the right images for the product on the first try. The Quanos InfoTwin is easy to use and allows for quick successes; existing BOMs can be quickly integrated and linked with the other data to form a catalog structure. In documentation we use Schema ST4, this data can also be integrated into InfoTwin without much effort.“
WILO SE Holger Danielzik | Spare Parts Documentation

No Internet? No Problem. The Companion App for Quanos InfoTwin
When connectivity drops, efficiency shouldn’t.
With the Offline Companion App, field technicians access spare parts catalogs, service instructions, and technical documentation from Quanos InfoTwin - anytime, anywhere, even without an internet connection.
Whether offshore, underground, or in remote facilities, the app ensures your service teams stay productive and resolve issues fast - no signal required.
Curious how it works and why offline access is critical? Read our blog article "Dead Spots - A Productivity Drain" now.
Explore features and benefits in our compact fact sheet:
Start transforming your aftersales & service processes now

Save time and costs – increased productivity
- Global access to all of the necessary information at any time thanks to cloud service
- Networked information from various data sources
- Smart Search – find the right information quickly and easily
- Service activity wizard including overview of necessary spare parts and tools

Smart services and new business models
- Develop new business and accounting models based on assets and products
- Flexible expansion thanks to SaaS model – ready for smart services
- Simple integration into your own portals and apps via TwinAPI
- Target group-specific distribution of service documentation incl. monetization option
Need to talk about it?
- Do you have optimized aftersales & service processes and the current status of your machines and plants at a glance?
- Do you have all of the necessary information including the spare part needed to eliminate the fault in your hands quickly and efficiently?
- Are you able to develop new business models with a digital model of your machine?
No? Then start transforming your aftersales & service processes now!
Make an appointment with an expert today!
Function sets & integrations – tailored to your needs
AI functions in Quanos InfoTwin: Intelligent data, smart service
InfoTwin AI Assistant: The future of data interaction

InfoTwin AI Assistant boasts a user-friendly chat interface that simplifies communication with your data. Just ask a question, and the AI delivers accurate answers relevant to the specific product or asset – based on your content and the comprehensive information contained in the Quanos InfoTwin knowledge model. Thanks to the RAG architecture, answers are always reliable and based exclusively on the authoritative document content stored in InfoTwin. This essentially eliminates the risk that you'll get incorrect information.
InfoTwin AI Assistant is currently being validated with selected customers as part of the pilot phase. Want to take part in the pilot phase as well?
plusmeta AI Connector: Smart data preparation made easy

If you're looking to integrate and structure your supplier data and existing documentation, it's a breeze with plusmeta AI Connector. The cloud-based plusmeta AI platform reads your unstructured data (such as PDFs), analyzes them, and automatically incorporates metadata based on a range of AI technologies. Even older documentation, or large volumes of it, is efficiently classified and structured so it can be used to best effect InfoTwin. Result: Your data become smarter, and are available exactly where you need them – for a digital information twin that really does more.
Frequently asked questions about Quanos InfoTwin:
Quanos InfoTwin is a modular software-as-a-service solution for machine and plant construction that brings together all the information contained in technical documentation, spare parts management, and other sources of product and customer information in the cloud. The platform networks this information to create a digital information twin that provides aftersales and service teams with current and accurate data at all times – no matter whether they’re looking for spare parts, the right operating instructions for a maintenance job, or details about consumables that will be needed in the near future.
Quanos InfoTwin is an important tool for customer service employees and service technicians who need access to the right information at the right time, for instance in meetings with customers, or when out and about on field service assignments. A digital information twin consolidates expertise right the way from plant to spare parts level. As such, it also forms the basis for self-service portals, which customers can use to access information they need.
Quanos InfoTwin was developed for manufacturers and operators who are looking to organize growing volumes of data on their machines and systems to make this information manageable and available in digital form.
Companies with complex products and extensive service processes benefit in particular from centrally networked information that they can make accessible to different stakeholders.
Essentially, Quanos InfoTwin is suitable for all industries and machine construction companies seeking to digitize their service processes and ease their employees' workload at a time when skilled staff are in short supply.
A platform for aftersales and service teamed with content delivery:
-
links relevant information that was previously dispersed throughout the company and makes it centrally available to technicians, support staff, and customers
-
reduces the requirement for manual intervention, for example when preparing data
-
supports technicians with expertise, visualizations, and assistance functions during field service assignments
-
networks information about machines and components with the technical documentation
-
makes it easier to identify spare parts in order to expedite repairs and minimize downtime
Successful machine and plant manufacturers not only sell high-quality machines and components, they also help their customers get the most out of their products for the long term.
Efficiency in operation, maintenance, and servicing requires data – which Quanos InfoTwin makes centrally available. This will allow you to maximize your service efficiency, reduce mistakes in orders, and offer your customers digital value-added services, such as a self-service portal, and new business and billing models that generate additional revenue.
Quanos InfoTwin represents good value for money for machine manufacturers of varying sizes across a number of industries. The software solution delivers the fastest return on investment to companies that are just embarking on their digital transformation process, and are looking to synchronize and automate their aftersales and service processes as efficiently as possible.
However, Quanos InfoTwin is also a solid investment for companies that have already implemented digital service processes and want to network their data sources and information even more effectively.
Feel free to get in touch with us if you wish to find out more about the potential savings Quanos InfoTwin can deliver for your company: Arrange a no-obligation consultation
Yes, depending your preferences, Quanos InfoTwin can combine the advantages of a SaaS solution with the power of AI. With the InfoTwin AI Assistant, your service and support employees have access to networked data from aftersales, service, and technical documentation in real time – such as via a chat interface. This allows them to find the information they are looking for faster.
And because Quanos InfoTwin is a modular cloud solution, you benefit from updates that incorporate current technology trends or new regulatory requirements, while having the option to add AI functions at any time.
You can quickly get started with Quanos InfoTwin – as a standardized and intuitive out-of-the-box solution, the platform is ready for use in no time. Its modular structure allows you to get started with the functions that are essential for you, after which you can expand and adapt the platform a step at a time.
Concerned about the quality of your data being up to scratch? There’s no need to worry, because Quanos InfoTwin helps you to consolidate existing data from different sources and improve its quality. Find out more in our practical guide to data quality.
Yes – thanks to the open API (TwinAPI) you can easily integrate Quanos InfoTwin into your company's software landscape and expand it effortlessly. So, you can connect Quanos InfoTwin with company portals, service apps, your ERP and other systems; this will save you the laborious task of searching for information across different logins, servers, and data formats.
Just like you, here at Quanos we consider first-rate customer support to be key. If you need special integration options or functions, or you require support with the software, you can put in a support request at any time via our ticket system and we will contact you directly to deal with your issue or inquiry.
The biggest advantage of a centralized aftersales and service platform is the availability of data in a central location; when service technicians carry out maintenance on your customers' plants, they no longer have to think about where to find the information they need. Instead, thanks to interactive step-by-step instructions and direct access to the required spare parts and tools, they will always know how to proceed next.
This optimizes your service processes and increases not only your first-time fix rate, but first and foremost customer satisfaction.
Yes, absolutely! We offer two options that let you familiarize yourself with the platform and its functions:
- Online demo environment: Simply request your demo access credentials and explore Quanos InfoTwin on your own in an interactive environment.
- Personal demo: If you have specific questions about the platform, it’s best to book a personal consultation. One of our experts will introduce the software to you in detail and show you how Quanos InfoTwin can help with your specific challenges.
Feel free to choose the option that suits you best!